

Raman spectroscopy: A tool for host response and virus characterisation
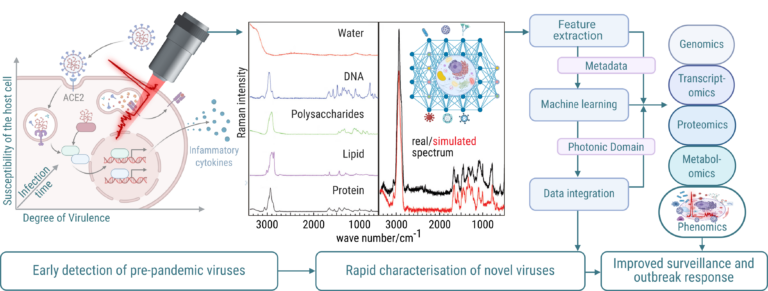
Its rapid, label-free measurements provide a versatile tool for investigating the changes in a cell’s morphochemical pattern, which controls many key processes during infection. Modern Raman-based analyses leverage machine learning to integrate spectral information within the biological context, revealing biochemical changes that drive phenotypic adaptations during infection – opening new dimensions for rapidly understanding underlying virus tropism. Building on established Raman spectroscopic fingerprinting of bacterial infections, we aim to extend this powerful technique to virus systems, offering rapid, scalable, and reproducible insights essential for pandemic preparedness, early detection of emerging pathogens, and zoonotic disease surveillance. By leveraging advanced Raman spectroscopic workflows combined with machine learning algorithms, the project aims to translate complex spectral data into actionable phenotypic insights. To ensure reproducibility and comparability, we will establish standardised and rigorously validated sample preparation protocols optimised specifically for Raman analysis, providing a robust foundation for elucidating virus infection cycles. Crucially, the tool we develop will systematically integrate Raman spectroscopy data with multiomics datasets (genomic, transcriptomic, proteomic, and metabolomic) for the analysis of virus interactions across different host systems by investigating infections with the eukaryotic virus SARS-CoV-2 and the vibriophage N4.
- WP 1: Raman spectroscopy platform optimised for virus research in the eukaryotic domain (Beer/Popp)
- WP 2: Raman spectroscopy platform optimised for virus research in the prokaryotic domain (Popp)
- WP 3: Technological benchmark for the label-free characterisation of virus particles (Popp/Beer)
Team Members

N. N.
Doctoral Researcher

N. N.
Doctoral Researcher

Doreen Schulz
Associated Technician

Sophie Girnius
Associated Lab Assistant
Project-Specific Publications
2025
Ramoji, Anuradha; Baumbach, Philipp; Ryabchykov, Oleg; Pistiki, Aikaterini; Rueger, Jan; Pinzon, David Vasquez; Silge, Anja; Deinhardt-Emmer, Stefanie; Schie, Iwan W; Weber, Karina; Neu, Charles; Neugebauer, Ute; Kiehntopf, Michael; Bocklitz, Thomas; Popp, Juergen; Coldewey, Sina M.
In: Biotechnology Journal, vol. 20, no. 9, pp. e70105, 2025.
@article{ramoji2025raman,
title = {Raman Spectroscopy Can Identify Acute and Persistent Biochemical Changes in Leukocytes From Patients With COVID-19 and Non-COVID-19-Associated Sepsis},
author = {Anuradha Ramoji and Philipp Baumbach and Oleg Ryabchykov and Aikaterini Pistiki and Jan Rueger and David Vasquez Pinzon and Anja Silge and Stefanie Deinhardt-Emmer and Iwan W Schie and Karina Weber and Charles Neu and Ute Neugebauer and Michael Kiehntopf and Thomas Bocklitz and Juergen Popp and Sina M. Coldewey},
url = {https://analyticalsciencejournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/biot.70105},
doi = {10.1002/biot.70105},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-01-01},
urldate = {2025-01-01},
journal = {Biotechnology Journal},
volume = {20},
number = {9},
pages = {e70105},
publisher = {Wiley Online Library},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2021
Wernike, Kerstin; Reimann, Ilona; Banyard, Ashley C; Kraatz, Franziska; Rocca, S Anna La; Hoffmann, Bernd; McGowan, Sarah; Hechinger, Silke; Choudhury, Bhudipa; Aebischer, Andrea; Steinbach, Falko; Beer, Martin
High genetic variability of Schmallenberg virus M-segment leads to efficient immune escape from neutralizing antibodies Journal Article
In: PLoS pathogens, vol. 17, no. 1, pp. e1009247, 2021.
@article{wernike2021high,
title = {High genetic variability of Schmallenberg virus M-segment leads to efficient immune escape from neutralizing antibodies},
author = {Kerstin Wernike and Ilona Reimann and Ashley C Banyard and Franziska Kraatz and S Anna La Rocca and Bernd Hoffmann and Sarah McGowan and Silke Hechinger and Bhudipa Choudhury and Andrea Aebischer and Falko Steinbach and Martin Beer },
url = {https://journals.plos.org/plospathogens/article?id=10.1371/journal.ppat.1009247},
doi = {10.1371/journal.ppat.1009247},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-01-01},
urldate = {2021-01-01},
journal = {PLoS pathogens},
volume = {17},
number = {1},
pages = {e1009247},
publisher = {Public Library of Science San Francisco, CA USA},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Guo, Shuxia; Popp, Jürgen; Bocklitz, Thomas
Chemometric analysis in Raman spectroscopy from experimental design to machine learning–based modeling Journal Article
In: Nature protocols, vol. 16, no. 12, pp. 5426–5459, 2021.
@article{guo2021chemometric,
title = {Chemometric analysis in Raman spectroscopy from experimental design to machine learning–based modeling},
author = {Shuxia Guo and Jürgen Popp and Thomas Bocklitz},
url = {https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-021-00620-3},
doi = {10.1038/s41596-021-00620-3},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-01-01},
urldate = {2021-01-01},
journal = {Nature protocols},
volume = {16},
number = {12},
pages = {5426–5459},
publisher = {Nature Publishing Group UK London},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2020
Dalmann, Anja; Reimann, Ilona; Wernike, Kerstin; Beer, Martin
Autonomously replicating RNAs of Bungowannah pestivirus: ERNS is not essential for the generation of infectious particles Journal Article
In: Journal of Virology, vol. 94, no. 14, pp. 10–1128, 2020.
@article{dalmann2020autonomously,
title = {Autonomously replicating RNAs of Bungowannah pestivirus: ERNS is not essential for the generation of infectious particles},
author = {Anja Dalmann and Ilona Reimann and Kerstin Wernike and Martin Beer},
url = {https://journals.asm.org/doi/full/10.1128/jvi.00436-20},
doi = {10.1128/jvi.00436-20},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-01-01},
urldate = {2020-01-01},
journal = {Journal of Virology},
volume = {94},
number = {14},
pages = {10–1128},
publisher = {American Society for Microbiology 1752 N St., NW, Washington, DC},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Thamamongood, Thiprampai; Aebischer, Andrea; Wagner, Valentina; Chang, Max W; Elling, Roland; Benner, Christopher; García-Sastre, Adolfo; Kochs, Georg; Beer, Martin; Schwemmle, Martin
A genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screen reveals the requirement of host cell sulfation for Schmallenberg virus infection Journal Article
In: Journal of Virology, vol. 94, no. 17, pp. 10–1128, 2020.
@article{thamamongood2020genome,
title = {A genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screen reveals the requirement of host cell sulfation for Schmallenberg virus infection},
author = {Thiprampai Thamamongood and Andrea Aebischer and Valentina Wagner and Max W Chang and Roland Elling and Christopher Benner and Adolfo García-Sastre and Georg Kochs and Martin Beer and Martin Schwemmle},
url = {https://journals.asm.org/doi/full/10.1128/jvi.00752-20},
doi = {10.1128/jvi.00752-20},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-01-01},
urldate = {2020-01-01},
journal = {Journal of Virology},
volume = {94},
number = {17},
pages = {10–1128},
publisher = {American Society for Microbiology 1752 N St., NW, Washington, DC},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Arend, Natalie; Pittner, Angelina; Ramoji, Anuradha; Mondol, Abdullah S; Dahms, Marcel; Rüger, Jan; Kurzai, Oliver; Schie, Iwan W; Bauer, Michael; Popp, Jürgen; Neugebauer, Ute
Detection and differentiation of bacterial and fungal infection of neutrophils from peripheral blood using Raman spectroscopy Journal Article
In: Analytical chemistry, vol. 92, no. 15, pp. 10560–10568, 2020.
@article{arend2020detection,
title = {Detection and differentiation of bacterial and fungal infection of neutrophils from peripheral blood using Raman spectroscopy},
author = {Natalie Arend and Angelina Pittner and Anuradha Ramoji and Abdullah S Mondol and Marcel Dahms and Jan Rüger and Oliver Kurzai and Iwan W Schie and Michael Bauer and Jürgen Popp and Ute Neugebauer},
url = {https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c01384?casa_token=W6h2sLYCDKUAAAAA%3Ak06HyQJye97UFNq9AuQC_o8YlYkP4hn_bBQfFP2XLLDhT8xPWCllNdeJt0WVRBPzc_IKYBhJeTJHQLQ},
doi = {10.1021/acs.analchem.0c01384.},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-01-01},
urldate = {2020-01-01},
journal = {Analytical chemistry},
volume = {92},
number = {15},
pages = {10560–10568},
publisher = {ACS Publications},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Deckert, Volker; Deckert-Gaudig, Tanja; Cialla-May, Dana; Popp, Jürgen; Zell, Roland; Deinhard-Emmer, Stefanie; Sokolov, Alexei V; Yi, Zhenhuan; Scully, Marlan O
Laser spectroscopic technique for direct identification of a single virus I: FASTER CARS Journal Article
In: Proc Natl Acad Sci, vol. 117, iss. 45, pp. 27820–27824, 2020.
@article{Deckert:20,
title = {Laser spectroscopic technique for direct identification of a single virus I: FASTER CARS},
author = { Volker Deckert and Tanja Deckert-Gaudig and Dana Cialla-May and Jürgen Popp and Roland Zell and Stefanie Deinhard-Emmer and Alexei V Sokolov and Zhenhuan Yi and Marlan O Scully},
url = {https://www.pnas.org/doi/abs/10.1073/pnas.2013169117},
doi = {10.1073/pnas.2013169117},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-01-01},
urldate = {2020-01-01},
journal = {Proc Natl Acad Sci},
volume = {117},
issue = {45},
pages = {27820–27824},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2018
Kirchhoff, Johanna; Glaser, Uwe; Bohnert, Jürgen A; Pletz, Mathias W; Popp, Jürgen; Neugebauer, Ute
Simple ciprofloxacin resistance test and determination of minimal inhibitory concentration within 2 h using Raman spectroscopy Journal Article
In: Analytical chemistry, vol. 90, no. 3, pp. 1811–1818, 2018.
@article{kirchhoff2018simple,
title = {Simple ciprofloxacin resistance test and determination of minimal inhibitory concentration within 2 h using Raman spectroscopy},
author = {Johanna Kirchhoff and Uwe Glaser and Jürgen A Bohnert and Mathias W Pletz and Jürgen Popp and Ute Neugebauer},
url = {https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b03800},
doi = {10.1021/acs.analchem.7b03800},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-01-01},
urldate = {2018-01-01},
journal = {Analytical chemistry},
volume = {90},
number = {3},
pages = {1811–1818},
publisher = {ACS Publications},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2015
Hoffmann, Bernd; Tappe, Dennis; Höper, Dirk; Herden, Christiane; Boldt, Annemarie; Mawrin, Christian; Niederstraßer, Olaf; Müller, Tobias; Jenckel, Maria; Grinten, Elisabeth; Lutter, Christian; Abendroth, Björn; Teifke, Jens P.; Cadar, Daniel; Schmidt-Chanasit, Jonas; Ulrich, Rainer G.; Beer, Martin
A variegated squirrel bornavirus associated with fatal human encephalitis Journal Article
In: New England Journal of Medicine, vol. 373, no. 2, pp. 154–162, 2015.
@article{hoffmann2015variegated,
title = {A variegated squirrel bornavirus associated with fatal human encephalitis},
author = {Bernd Hoffmann and Dennis Tappe and Dirk Höper and Christiane Herden and Annemarie Boldt and Christian Mawrin and Olaf Niederstraßer and Tobias Müller and Maria Jenckel and Elisabeth Grinten and Christian Lutter and Björn Abendroth and Jens P. Teifke and Daniel Cadar and Jonas Schmidt-Chanasit and Rainer G. Ulrich and Martin Beer},
url = {https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa1415627},
doi = {10.1056/NEJMoa1415627},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-01-01},
urldate = {2015-01-01},
journal = {New England Journal of Medicine},
volume = {373},
number = {2},
pages = {154–162},
publisher = {Mass Medical Soc},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2012
Hoffmann, Bernd; Scheuch, Matthias; Höper, Dirk; Jungblut, Ralf; Holsteg, Mark; Schirrmeier, Horst; Eschbaumer, Michael; Goller, Katja V; Wernike, Kerstin; Fischer, Melina; Breithaupt, Angele; Mettenleiter, Thomas C; Beer, Martin
Novel orthobunyavirus in cattle, Europe, 2011 Journal Article
In: Emerging infectious diseases, vol. 18, no. 3, pp. 469, 2012.
@article{hoffmann2012novel,
title = {Novel orthobunyavirus in cattle, Europe, 2011},
author = {Bernd Hoffmann and Matthias Scheuch and Dirk Höper and Ralf Jungblut and Mark Holsteg and Horst Schirrmeier and Michael Eschbaumer and Katja V Goller and Kerstin Wernike and Melina Fischer and Angele Breithaupt and Thomas C Mettenleiter and Martin Beer},
url = {https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3309600/},
doi = {10.3201/eid1803.111905},
year = {2012},
date = {2012-01-01},
urldate = {2012-01-01},
journal = {Emerging infectious diseases},
volume = {18},
number = {3},
pages = {469},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}



