
C01: High-resolution and high-throughput optical detection and characterisation of viruses

Projects of the CRC 1768

C01: High-resolution and high-throughput optical detection and characterisation of viruses
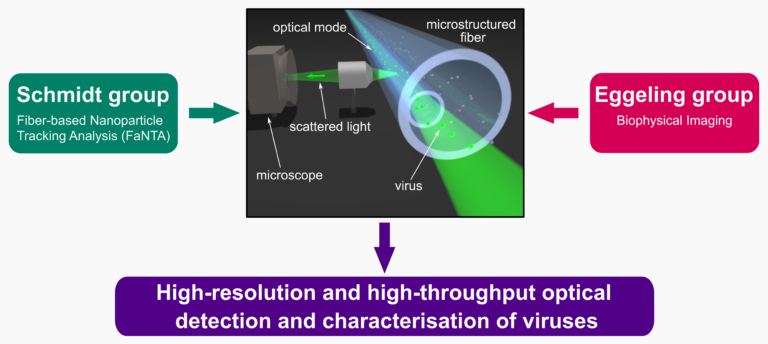
Here, the structural parameters of virus particles diffusing through a detection spot in an optical fiber or waveguide will be retrieved using measurements of elastic scattering and/or fluorescence emission. In this, the most challenging issues are the distinguishing of different viruses and of unwanted background material, which will be approached through optimisation of the fibers, correlation of readouts, and tailored data analysis. Specifically, we aim to employ a combination of label-free scattering-based detection and generic fluorescence labelling approaches, novel fiber technology, advanced scattering approaches, and fluorescence spectroscopy, and their joint detection and analysis. Analysis specifically includes a tailored interpretation of diffusional tracks, and we will openly share the analysis software. The long-term goal is to apply these methods to sort viruses. With this, we serve multiple research questions of the CRC VirusREvolution as well as the goals of virus description (G1, G3) and prediction of virus infectivity (G4).
Project Overview
- Tool to be developed: Expansion of the optical readouts and data analysis of fiber-based flow cytometry, termed (FaNTA), to maximise its sensitivity towards label-free or generic labelling-based morphological classification and potential sorting of viruses.
Hypothesis enabled by the proposed tool: A fast and label-free or generic labelling-based identification of morphological factors such as number, size, shape, and surface properties enables the classification and sorting of viruses and bacteriophages, with the aim of potentially linking them to their pathogenic potential.
Overarching CRC goals: Our project C01 advances FaNTA, a fiber-assisted nanoparticle tracking platform that
signatures of single virions at high throughput for rapid morpho-mechanical classification and sorting (G1, G3).
Quantifying morphotype distributions across variants and contexts provides phenotypic readouts that support
evolutionary comparisons and feed predictive models of infectivity/tropism for early triage (G4).
Work Packages (WP):
- WP 1: Adaptation and optimisation of the FaNTA tool on training viruses (Schmidt)
- WP 2: Expansion of the FaNTA tool with a fluorescence readout
- WP 3: Expansion of the FaNTA tool with the iSCAT readout (Eggeling/Schmidt)
Team Members
2025
Reina, Francesco; Eggeling, Christian; Lagerholm, Christoffer
High‐Speed Interferometric Scattering Tracking Microscopy of Compartmentalized Lipid Diffusion in Living Cells Journal Article
In: ChemPhysChem, vol. 26, 2025.
@article{articlef,
title = {High‐Speed Interferometric Scattering Tracking Microscopy of Compartmentalized Lipid Diffusion in Living Cells},
author = {Francesco Reina and Christian Eggeling and Christoffer Lagerholm},
doi = {10.1002/cphc.202400407},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-01-01},
urldate = {2025-01-01},
journal = {ChemPhysChem},
volume = {26},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Reina, Francesco; Saavedra, Lucas; Eggeling, Christian; Barrantes, Francisco
In: Nature Communications, vol. 16, 2025.
@article{articlei,
title = {Concurrent diffusion of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and fluorescent cholesterol disclosed by two-colour sub-millisecond MINFLUX-based single-molecule tracking},
author = {Francesco Reina and Lucas Saavedra and Christian Eggeling and Francisco Barrantes},
doi = {10.1038/s41467-025-61489-4},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-01-01},
urldate = {2025-01-01},
journal = {Nature Communications},
volume = {16},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2024
Angelis, Giovanni; Abramo, Jacopo; Miasnikova, Mariia; Taubert, Marcel; Eggeling, Christian; Reina, Francesco
Homogeneous large field-of-view and compact iSCAT-TIRF setup for dynamic single molecule measurements Journal Article
In: Optics Express, vol. 32, pp. 46607-46620, 2024.
@article{articlee,
title = {Homogeneous large field-of-view and compact iSCAT-TIRF setup for dynamic single molecule measurements},
author = {Giovanni Angelis and Jacopo Abramo and Mariia Miasnikova and Marcel Taubert and Christian Eggeling and Francesco Reina},
doi = {10.1364/OE.532947},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-01-01},
urldate = {2024-01-01},
journal = {Optics Express},
volume = {32},
pages = {46607-46620},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Seltmann, Alexander; Carravilla, Pablo; Reglinski, Katharina; Eggeling, Christian; Waithe, Dominic
Neural network informed photon filtering reduces fluorescence correlation spectroscopy artifacts Journal Article
In: Biophysical Journal, vol. 123, 2024.
@article{articleg,
title = {Neural network informed photon filtering reduces fluorescence correlation spectroscopy artifacts},
author = {Alexander Seltmann and Pablo Carravilla and Katharina Reglinski and Christian Eggeling and Dominic Waithe},
doi = {10.1016/j.bpj.2024.02.012},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-01-01},
urldate = {2024-01-01},
journal = {Biophysical Journal},
volume = {123},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2023
Wieduwilt, Torsten; Förster, Ronny; Nissen, Mona; Kobelke, Jens; Schmidt, Markus
Characterization of diffusing sub-10 nm nano-objects using single anti-resonant element optical fibers Journal Article
In: Nature Communications, vol. 14, 2023.
@article{articlec,
title = {Characterization of diffusing sub-10 nm nano-objects using single anti-resonant element optical fibers},
author = {Torsten Wieduwilt and Ronny Förster and Mona Nissen and Jens Kobelke and Markus Schmidt},
doi = {10.1038/s41467-023-39021-3},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-01-01},
urldate = {2023-01-01},
journal = {Nature Communications},
volume = {14},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Svensson, Carl; Reglinski, Katharina; Schliebs, Wolfgang; Erdmann, Ralf; Eggeling, Christian; Figge, Marc
Quantitative analysis of peroxisome tracks using a Hidden Markov Model Journal Article
In: Scientific Reports, vol. 13, 2023.
@article{articleh,
title = {Quantitative analysis of peroxisome tracks using a Hidden Markov Model},
author = {Carl Svensson and Katharina Reglinski and Wolfgang Schliebs and Ralf Erdmann and Christian Eggeling and Marc Figge},
doi = {10.1038/s41598-023-46812-7},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-01-01},
urldate = {2023-01-01},
journal = {Scientific Reports},
volume = {13},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2022
Nissen, Mona; Förster, Ronny; Wieduwilt, Torsten; Lorenz, Adrian; Jiang, Shiqi; Hauswald, Walter; Schmidt, Markus
Nanoparticle Tracking in Single‐Antiresonant‐Element Fiber for High‐Precision Size Distribution Analysis of Mono‐ and Polydisperse Samples Journal Article
In: Small, vol. 18, pp. 2202024, 2022.
@article{articleb,
title = {Nanoparticle Tracking in Single‐Antiresonant‐Element Fiber for High‐Precision Size Distribution Analysis of Mono‐ and Polydisperse Samples},
author = {Mona Nissen and Ronny Förster and Torsten Wieduwilt and Adrian Lorenz and Shiqi Jiang and Walter Hauswald and Markus Schmidt},
doi = {10.1002/smll.202202024},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-01-01},
urldate = {2022-01-01},
journal = {Small},
volume = {18},
pages = {2202024},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2021
Gui, Fengji; Jiang, Shiqi; Förster, Ronny; Plidschun, Malte; Weidlich, Stefan; Zhao, Jiangbo; Schmidt, Markus
Ultralong Tracking of Fast diffusing Nano‐Objects Inside Nano‐Fluidic Channel Enhanced Microstructured Optical Fiber Journal Article
In: Advanced Photonics Research, vol. 2, pp. 2100032, 2021.
@article{article,
title = {Ultralong Tracking of Fast diffusing Nano‐Objects Inside Nano‐Fluidic Channel Enhanced Microstructured Optical Fiber},
author = {Fengji Gui and Shiqi Jiang and Ronny Förster and Malte Plidschun and Stefan Weidlich and Jiangbo Zhao and Markus Schmidt},
doi = {10.1002/adpr.202100032},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-01-01},
urldate = {2021-01-01},
journal = {Advanced Photonics Research},
volume = {2},
pages = {2100032},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2020
Förster, Ronny; Weidlich, Stefan; Nissen, Mona; Wieduwilt, Torsten; Kobelke, Jens; Goldfain, Aaron; Chiang, Timothy; Garmann, Rees; Manoharan, Vinothan; Lahini, Yoav; Schmidt, Markus
Tracking and Analyzing the Brownian Motion of Nano-objects Inside Hollow Core Fibers Journal Article
In: ACS Sensors, vol. XXXX, 2020.
@article{articled,
title = {Tracking and Analyzing the Brownian Motion of Nano-objects Inside Hollow Core Fibers},
author = {Ronny Förster and Stefan Weidlich and Mona Nissen and Torsten Wieduwilt and Jens Kobelke and Aaron Goldfain and Timothy Chiang and Rees Garmann and Vinothan Manoharan and Yoav Lahini and Markus Schmidt},
doi = {10.1021/acssensors.0c00339},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-01-01},
urldate = {2020-01-01},
journal = {ACS Sensors},
volume = {XXXX},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2015
Faez, Sanli; Lahini, Yoav; Weidlich, Stefan; Garmann, Rees F.; Wondraczek, Katrin; Zeisberger, Matthias; Schmidt, Markus A.; Orrit, Michel; Manoharan, Vinothan N.
Fast, Label-Free Tracking of Single Viruses and Weakly Scattering Nanoparticles in a Nanofluidic Optical Fiber Journal Article
In: ACS Nano, vol. 9, no. 12, pp. 12349-12357, 2015, (PMID: 26505649).
@article{doi:10.1021/acsnano.5b05646,
title = {Fast, Label-Free Tracking of Single Viruses and Weakly Scattering Nanoparticles in a Nanofluidic Optical Fiber},
author = {Sanli Faez and Yoav Lahini and Stefan Weidlich and Rees F. Garmann and Katrin Wondraczek and Matthias Zeisberger and Markus A. Schmidt and Michel Orrit and Vinothan N. Manoharan},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b05646},
doi = {10.1021/acsnano.5b05646},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-01-01},
urldate = {2015-01-01},
journal = {ACS Nano},
volume = {9},
number = {12},
pages = {12349-12357},
note = {PMID: 26505649},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}


