
A04: Small RNAs to probe, decode, and optimise phage-host interactions

Projects of the CRC 1768

A04: Small RNAs to probe, decode, and optimise phage-host interactions
Regulatory RNAs have emerged as powerful tools in synthetic biology due to their programmability and ability to modulate gene expression with high specificity. Among these, small RNAs (sRNAs) that act through base-pairing interactions offer a versatile platform for controlling molecular processes in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems. Indeed, synthetic regulatory RNAs have already shown potential in metabolic engineering, gene regulation, and diagnostics. However, despite their broad regulatory utility, synthetic regulatory RNAs have not yet been broadly applied to antiviral strategies, especially those targeting RNA-RNA interactions relevant during viral infection. In viruses, RNA structures and RNA-mediated gene regulation are closely linked to replication and host manipulation, making them attractive targets for RNA-based interference. However, rationally designing effective synthetic RNAs remains a major challenge due to the complexity of RNA folding, target recognition, and the dynamic nature of virus host interactions.
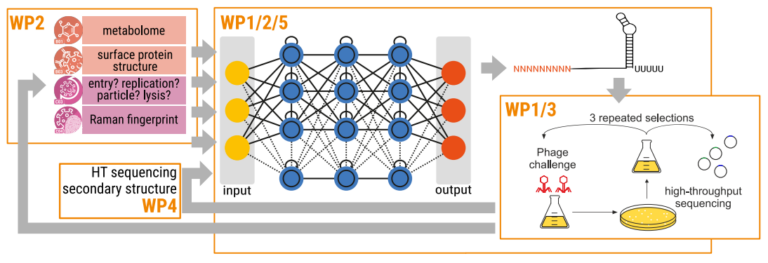
All of the WPs are contributing via an integrated approach to the iterative development of our NN to study phage-host interactions
Recent advances in the design of synthetic regulatory RNAs and machine learning, particularly neural networks (NN), now offer a path towards predictive modelling of these interactions. Furthermore, integrating experimental feedback into model training holds promise for accelerating the design-test-learn cycle of the synthetic biology toolbox. In this project, we aim to close this gap by systematically and adaptively optimising antiviral RNAs that target viral and/or host RNAs that are required for virus infection and replication. Specifically, we will develop a neural network- based tool that integrates predictive modelling of RNA-RNA interactions with experimental feedback to optimise synthetic antiviral RNAs. The tool will focus on targeting both coding and non-coding features of viral and host RNAs to disrupt viral entry, replication, and exit. Our initial work will concentrate on bacteriophages, with future expansion to eukaryotic viruses.
The tool will learn from wet-lab data to improve predictions of functional RNA interactions and guide the identification of more potent RNA molecules in iterative cycles. By modelling both interacting and non-interacting RNA pairs, the system will distinguish functional mechanisms from background noise, increasing design accuracy. Through collaborations within the CRC VirusREvolution consortium, the neural network will be enhanced with diverse datasets, improving its generalisability across different phage-host systems following the overall topics G2 and G3.
The resulting platform will provide the foundation for programmable RNA therapeutics with high specificity, adaptability, and reduced likelihood of resistance. It will also establish general principles for RNA-mediated antiviral defence that can be leveraged across different organisms and viral families.
From a broader perspective, this project bridges computational and experimental biology to tackle one of the central challenges in virology and synthetic biology – how to rationally design molecules that can interfere with evolving viral systems. This strategy goes beyond classical design principles and opens avenues for responsive, data-driven synthetic biology. Taken together, the proposed work will (a) advance our understanding of viral adsorption, entry, replication, and escape; (b) support the long-term goal of intelligent, programmable, and adaptive biological interventions; and (c) provide novel intervention strategies targeting viruses at the RNA level. This aligns closely with the overarching research goals of the CRC: understanding of virus evolution (G2), virus-host interactions (G3), and the mechanisms of viral infection (G4).
Project Overview
This project aims to develop and iteratively refine neural network (NN) architectures capable of predicting and optimising synthetic antiviral small RNAs (sRNAs) of arbitrary length. By integrating high-throughput functional screens with multi-omic, structural, and biophysical datasets, we will establish a comprehensive modelling framework that captures the complexity of phage-host interactions. Ultimately, this will provide both mechanistic insights into antiviral resistance and practical strategies for rational sRNA design.
The resulting tools will enable programmable, rational design of antiviral RNAs, with high adaptability to evolving viral threats. This significantly improves speed and precision of antiviral development. Beyond this project, the approach can be generalised to design RNAs for other purposes, such as synthetic gene regulation, diagnostics, or metabolic control. This project bridges computational prediction and experimental validation, creating a closed loop between dry-lab and wet-lab. It contributes to the broader vision of intelligent biological design systems, where models learn directly from functional outputs. The methodology aligns with the growing need for responsive, modular antiviral technologies, especially during pandemic threats. By creating a system developed to learn across viruses and hosts, we lay the groundwork for adaptive synthetic biology platforms. Ultimately, this work aims at a paradigm shift in virology and RNA biology – away from static analyses and toward dynamic, data-driven tools capable of real-time optimisation and design. The project stands at the intersection of systems biology, AI, and molecular virology.
- Tool to be developed: An NN-driven, user-friendly platform with an integrated wet-lab feedback loop that predicts and iteratively optimises antiviral sRNAs from sequence and minimal experimental input, enabling in the future even BSL-3/4 laboratories to identify potent candidates without exhaustive screening.
- Tool to be developed: A computational tool that predicts RNA-RNA interactions by learning distinguishing features from non-interacting RNA pairs.
Hypothesis enabled by the proposed tool: By comparing multiple virus-host systems, we can uncover general principles of RNA-mediated resistance that are transferable across different viral contexts.
Overarching CRC goals: Our project builds a feedback-coupled NN to design and optimise synthetic small RNAs that target viral and host RNAs, thereby decoding generalisable rules of RNA-mediated virus-host interaction systems (G3) and revealing evolutionary escape routes under targeted perturbation (G2). The resulting models provide predictive estimates of infection (G4).
Work Packages (WP):
- WP 1: NN architecture design for optimising synthetic short RNAs (Marz/Papenfort)
- WP 2: Extended neural network (Marz/Papenfort)
- WP 3: Comparing dozens of phage-host systems to identify general principles of resistance (Papenfort)
- WP 4: Improved identification of RNA-RNA interactions (Marz)
- WP 5: Targeting eukaryotic viruses by optimising antiviral RNA-RNA interactions (Marz)
Team Members
Project- and subject-related list of publications
2024
Triebel, Sandra; Lamkiewicz, Kevin; Ontiveros, Nancy; Sweeney, Blake; Stadler, Peter F.; Petrov, Anton I; Niepmann, Michael; Marz, Manja
Comprehensive survey of conserved RNA secondary structures in full-genome alignment of hepatitis C virus Journal Article
In: Sci. Rep., vol. 14, iss. 1, pp. 15145, 2024, ISSN: 2045-2322.
@article{Triebel:24,
title = {Comprehensive survey of conserved RNA secondary structures in full-genome alignment of hepatitis C virus},
author = {Sandra Triebel and Kevin Lamkiewicz and Nancy Ontiveros and Blake Sweeney and Peter F. Stadler and Anton I Petrov and Michael Niepmann and Manja Marz},
url = {https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38956134/},
doi = {10.1038/s41598-024-62897-0},
issn = {2045-2322},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-07-01},
journal = {Sci. Rep.},
volume = {14},
issue = {1},
pages = {15145},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {epublish},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Sprenger, Marcel; Siemers, Malte; Krautwurst, Sebastian; Papenfort, Kai
Small RNAs direct attack and defense mechanisms in a quorum sensing phage and its host. Journal Article
In: Cell Host Microbe, vol. 32, iss. 5, pp. 727–738.e6, 2024.
@article{Sprenger:24,
title = {Small RNAs direct attack and defense mechanisms in a quorum sensing phage and its host.},
author = {Marcel Sprenger and Malte Siemers and Sebastian Krautwurst and Kai Papenfort},
url = {https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38579715/},
doi = {10.1016/j.chom.2024.03.010},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-05-01},
journal = {Cell Host Microbe},
volume = {32},
issue = {5},
pages = {727–738.e6},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {ppublish},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2022
Huber, Michaela; Lippegaus, Anne; Melamed, Sahar; Siemers, Malte; Wucher, Benjamin R.; Hoyos, Mona; Nadell, Carey; Storz, Gisela; Papenfort, Kai
An RNA sponge controls quorum sensing dynamics and biofilm formation in emphVibrio cholerae Journal Article
In: Nat Commun, vol. 13, no. 7585, 2022.
@article{Huber:22,
title = {An RNA sponge controls quorum sensing dynamics and biofilm formation in emphVibrio cholerae},
author = {Michaela Huber and Anne Lippegaus and Sahar Melamed and Malte Siemers and Benjamin R. Wucher and Mona Hoyos and Carey Nadell and Gisela Storz and Kai Papenfort},
doi = {10.1038/s41467-022-35261-x},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-01-01},
journal = {Nat Commun},
volume = {13},
number = {7585},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Mock, Florian; Kretschmer, Fleming; Kriese, Anton; Böcker, Sebastian; Marz, Manja
Taxonomic classification of DNA sequences beyond sequence similarity using deep neural networks Journal Article
In: Proc Natl Acad Sci, vol. 119, no. 35, 2022.
@article{Mock:22,
title = {Taxonomic classification of DNA sequences beyond sequence similarity using deep neural networks},
author = {Florian Mock and Fleming Kretschmer and Anton Kriese and Sebastian Böcker and Manja Marz},
doi = {10.1073/pnas.2122636119},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-01-01},
journal = {Proc Natl Acad Sci},
volume = {119},
number = {35},
publisher = {Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2021
Venkat, Kavyaa; Hoyos, Mona; Haycocks, James Rj; Cassidy, Liam; Engelmann, Beatrice; Rolle-Kampczyk, Ulrike; Bergen, Martin; Tholey, Andreas; Grainger, David C; Papenfort, Kai
A dual-function RNA balances carbon uptake and central metabolism in emphVibrio cholerae Journal Article
In: EMBO J, vol. 40, iss. 24, pp. e108542, 2021.
@article{Venkat:21,
title = {A dual-function RNA balances carbon uptake and central metabolism in emphVibrio cholerae},
author = {Kavyaa Venkat and Mona Hoyos and James Rj Haycocks and Liam Cassidy and Beatrice Engelmann and Ulrike Rolle-Kampczyk and Martin Bergen and Andreas Tholey and David C Grainger and Kai Papenfort},
doi = {10.15252/embj.2021108542},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-01-01},
journal = {EMBO J},
volume = {40},
issue = {24},
pages = {e108542},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Mock, Florian; Viehweger, Adrian; Barth, Emanuel; Marz, Manja
VIDHOP, viral host prediction with deep learning. Journal Article
In: Bioinformatics, vol. 37, iss. 3, pp. 318–325, 2021, ISSN: 1367-4811.
@article{Mock:21,
title = {VIDHOP, viral host prediction with deep learning.},
author = {Florian Mock and Adrian Viehweger and Emanuel Barth and Manja Marz},
doi = {10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa705},
issn = {1367-4811},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-01-01},
journal = {Bioinformatics},
volume = {37},
issue = {3},
pages = {318–325},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2020
Peschek, Nikolai; Herzog, Roman; Singh, Praveen K; Sprenger, Marcel; Meyer, Fabian; Fröhlich, Kathrin S; Schröger, Luise; Bramkamp, Marc; Drescher, Knut; Papenfort, Kai
RNA-mediated control of cell shape modulates antibiotic resistance in emphVibrio cholerae Journal Article
In: Nat Commun, vol. 11, iss. 1, pp. 6067, 2020.
@article{Peschek:20,
title = {RNA-mediated control of cell shape modulates antibiotic resistance in emphVibrio cholerae},
author = {Nikolai Peschek and Roman Herzog and Praveen K Singh and Marcel Sprenger and Fabian Meyer and Kathrin S Fröhlich and Luise Schröger and Marc Bramkamp and Knut Drescher and Kai Papenfort},
doi = {10.1038/s41467-020-19890-8},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-01-01},
journal = {Nat Commun},
volume = {11},
issue = {1},
pages = {6067},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2019
Peschek, Nikolai; Hoyos, Mona; Herzog, Roman; Förstner, Konrad U; Papenfort, Kai
A conserved RNA seed-pairing domain directs small RNA-mediated stress resistance in enterobacteria Journal Article
In: EMBO J, vol. 38, iss. 16, pp. e101650, 2019.
@article{Peschek:19,
title = {A conserved RNA seed-pairing domain directs small RNA-mediated stress resistance in enterobacteria},
author = {Nikolai Peschek and Mona Hoyos and Roman Herzog and Konrad U Förstner and Kai Papenfort},
doi = {10.15252/embj.2019101650},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-01-01},
journal = {EMBO J},
volume = {38},
issue = {16},
pages = {e101650},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Viehweger, Adrian; Krautwurst, Sebastian; Lamkiewicz, Kevin; Madhugiri, Ramakanth; Ziebuhr, John; Hölzer, Martin; Marz, Manja
In: Genome Res, vol. 29, iss. 9, pp. 1545–1554, 2019, ISSN: 1549-5469.
@article{Viehweger:19,
title = {Direct RNA nanopore sequencing of full-length coronavirus genomes provides novel insights into structural variants and enables modification analysis.},
author = {Adrian Viehweger and Sebastian Krautwurst and Kevin Lamkiewicz and Ramakanth Madhugiri and John Ziebuhr and Martin Hölzer and Manja Marz},
doi = {10.1101/gr.247064.118},
issn = {1549-5469},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-01-01},
journal = {Genome Res},
volume = {29},
issue = {9},
pages = {1545–1554},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2016
Fricke, Markus; Marz, Manja
Prediction of conserved long-range RNA-RNA interactions in full viral genomes Journal Article
In: Bioinformatics, vol. 32, iss. 19, pp. 2928–2935, 2016.
@article{Fricke:16,
title = {Prediction of conserved long-range RNA-RNA interactions in full viral genomes},
author = {Markus Fricke and Manja Marz},
doi = {10.1093/bioinformatics/btw323},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-01},
journal = {Bioinformatics},
volume = {32},
issue = {19},
pages = {2928–2935},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}



