
B01: Chemical mediators of virus infection
Projects of the CRC 1768

B01: Chemical mediators of virus infection
Metabolites are small molecules that participate in, and arise from, cellular metabolism. They span all chemical classes including sugars, amino acids, nucleotides, lipids, oxylipins and oxidised lipids, and many more. Metabolites show extensive structural diversity that is not dictated by polymeric templates. Beyond endogenously synthesised compounds, the metabolome also includes exogenous molecules and their biotransformation products. These metabolites can mediate interactions between cells and organisms of all phyla. The diversity, dynamic production, and turnover of metabolites make their analysis highly challenging. Because metabolites are key to understanding biological processes, including resistance to infection, their study is highly rewarding.
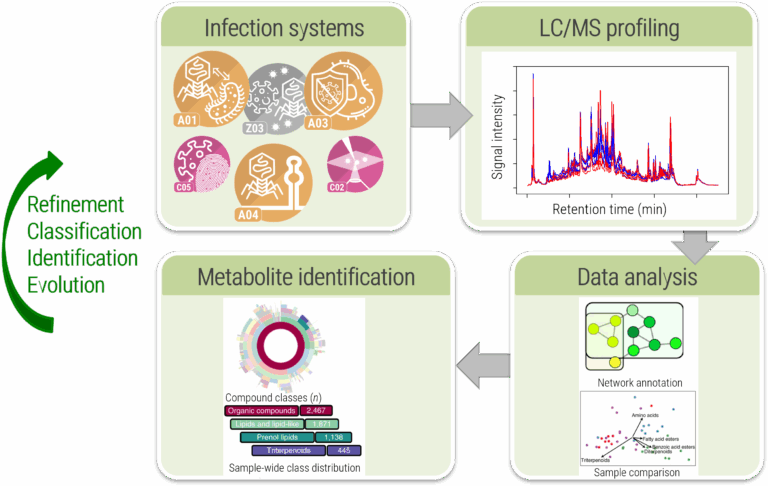
In this project, we will establish an experimental and computational platform for untargeted metabolomics that allows us to monitor the changes in metabolism induced by a virus infection, Fig. B01.1. We will develop experimental and computational methods that cover a broad range of small molecules. We will place a special focus on (modified) lipids and cyclic nucleotides in response to virus infections. These compound classes are central to virus infection processes, but notoriously difficult to investigate using current computational approaches. We will optimise analytical and computational methods side by side. Our computational methods will be made available via the well-established and frequently used SIRIUS platform from the Böcker lab5, and also integrated into the joint computational platform of the CRC VirusREvolution. We will use our platform to unravel intrinsic and induced metabolomic properties of virus infections and to monitor the associated, even subtle, changes in metabolism over time.
Project Overview
This project aims to provide methods to comprehensively analyse the metabolome of virus infections across diverse viruses and phages, Fig. B01.3. For infection models of this CRC, we will record endo- and exometabolomes from infection models and analyse the data with existing and novel computational tools to elucidate virus infection metabolism. We hypothesise that structural data on dysregulated metabolites will provide new mechanistic insights and therapeutic avenues. Beyond computation, we will develop experimental protocols to optimise biological experiments so that they become the foundation of high-quality metabolomic data sets. All methods will be developed collaboratively between bioinformaticians, analytical chemists, and CRC partners to ensure biological relevance.
We will advance computational methods for analysing lipids, oxylipins and oxidised lipids, modified nucleotides, and cyclic oligonucleotides, integrating them into our computational platform for broad metabolomic coverage. Each compound class will be addressed with specialised tools. For modified nucleotides, we will generate in silico biochemical variants and screen datasets using SIRIUS, CSI:FingerID and our own tool, COSMIC. Lipid analysis will build on El Gordo to annotate beyond library searches and include visualisations in SIRIUS for comparing healthy and infected samples, Fig. B01.4. Machine learning models will be developed for oxylipin analysis, expected to significantly enhance annotation quality. Again, results must be visualised to maximise information in a simple and appealing form.
We will also design new analytical and computational methods for short cyclic oligonucleotides, a key class in phage and virus infections. Since existing small-molecule tools are unsuitable, we will explore combinatorial optimisation (e.g. dynamic programming) and stochastic modelling combined with machine learning models. This will allow for structural inference, favouring simpler machine learning models that perform reliably with limited training data.
- Tool to be developed:An advanced tool for untargeted ecometabolomic monitoring and computational analysis of metabolomics data from virus infections, focusing, but not restricted to, on lipids, oxylipins and oxidised lipids, nucleotides, and cyclic oligonucleotides, seamlessly integrating MS-based analytics with powerful SIRIUS-driven data evaluation.
Hypothesis enabled by the proposed tool:
Overarching CRC goals:
Work Packages (WP):
- WP 1: Omics integration, untargeted experiments, and targeted verification (Pohnert, Böcker)
- WP 2: Computational analysis and interpretation of lipidomics and metabolomics data (Böcker, Pohnert)
- WP 3: Screening for modified nucleotides and cyclic oligonucleotides (Böcker/Pohnert)
- WP 4: Analysing complex biosystems and co-infections (Pohnert/Böcker)
Team Members
2025
Nikitashina, Vera; Bartels, Benjamin; Mansour, Joost Samir; LeKieffre, Charlotte; Decelle, Johan; Hertweck, Christian; Not, Fabrice; Pohnert, Georg
Metabolic interdependence and rewiring in radiolaria-microalgae photosymbioses. Journal Article
In: The ISME Journal, vol. 19, iss. 1, 2025.
@article{Nikitashina:25,
title = {Metabolic interdependence and rewiring in radiolaria-microalgae photosymbioses.},
author = {Vera Nikitashina and Benjamin Bartels and Joost Samir Mansour and Charlotte LeKieffre and Johan Decelle and Christian Hertweck and Fabrice Not and Georg Pohnert},
url = {https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40057976/},
doi = {10.1093/ismejo/wraf047},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-01-01},
journal = {The ISME Journal},
volume = {19},
issue = {1},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {ppublish},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2024
Deng, Yun; Yu, Ruyi; Grabe, Veit; Sommermann, Thomas; Werner, Markus; Vallet, Marine; Zerfaß, Christian; Werz, Oliver; Pohnert, Georg
Bacteria modulate microalgal aging physiology through the induction of extracellular vesicle production to remove harmful metabolites. Journal Article
In: Nat Microbiol, vol. 9, iss. 9, pp. 2356–2368, 2024.
@article{Deng:24,
title = {Bacteria modulate microalgal aging physiology through the induction of extracellular vesicle production to remove harmful metabolites.},
author = {Yun Deng and Ruyi Yu and Veit Grabe and Thomas Sommermann and Markus Werner and Marine Vallet and Christian Zerfaß and Oliver Werz and Georg Pohnert},
url = {https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39143356/},
doi = {10.1038/s41564-024-01746-2},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-09-01},
journal = {Nat Microbiol},
volume = {9},
issue = {9},
pages = {2356–2368},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {ppublish},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2022
Stravs, Michael A; Dührkop, Kai; Böcker, Sebastian; Zamboni, Nicola
MSNovelist: emphDe novo structure generation from mass spectra Journal Article
In: Nat Methods, vol. 19, iss. 7, no. 7, pp. 865–870, 2022.
@article{Stravs:22,
title = {MSNovelist: emphDe novo structure generation from mass spectra},
author = {Michael A Stravs and Kai Dührkop and Sebastian Böcker and Nicola Zamboni},
url = {https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35637304/},
doi = {10.1038/s41592-022-01486-3},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-07-01},
journal = {Nat Methods},
volume = {19},
number = {7},
issue = {7},
pages = {865–870},
publisher = {Springer Science and Business Media LLC},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {ppublish},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Hoffmann, Martin A; Nothias, Louis-Félix; Ludwig, Marcus; Fleischauer, Markus; Gentry, Emily C; Witting, Michael; Dorrestein, Pieter C; Dührkop, Kai; Böcker, Sebastian
High-confidence structural annotation of metabolites absent from spectral libraries Journal Article
In: Nat Biotechnol, vol. 40, pp. 411–421, 2022.
@article{Hoffmann:22,
title = {High-confidence structural annotation of metabolites absent from spectral libraries},
author = {Martin A Hoffmann and Louis-Félix Nothias and Marcus Ludwig and Markus Fleischauer and Emily C Gentry and Michael Witting and Pieter C Dorrestein and Kai Dührkop and Sebastian Böcker},
doi = {10.1038/s41587-021-01045-9},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-01-01},
journal = {Nat Biotechnol},
volume = {40},
pages = {411–421},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2021
Dührkop, Kai; Nothias, Louis-Félix; Fleischauer, Markus; Reher, Raphael; Ludwig, Marcus; Hoffmann, Martin A; Petras, Daniel; Gerwick, William H; Rousu, Juho; Dorrestein, Pieter C; Böcker, Sebastian
Systematic classification of unknown metabolites using high-resolution fragmentation mass spectra Journal Article
In: Nat Biotechnol, vol. 39, iss. 4, pp. 462–471, 2021.
@article{Duehrkop:21,
title = {Systematic classification of unknown metabolites using high-resolution fragmentation mass spectra},
author = {Kai Dührkop and Louis-Félix Nothias and Markus Fleischauer and Raphael Reher and Marcus Ludwig and Martin A Hoffmann and Daniel Petras and William H Gerwick and Juho Rousu and Pieter C Dorrestein and Sebastian Böcker},
doi = {10.1038/s41587-020-0740-8},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-01-01},
journal = {Nat Biotechnol},
volume = {39},
issue = {4},
pages = {462–471},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2019
Vallet, Marine; Baumeister, Tim U H; Kaftan, Filip; Grabe, Veit; Buaya, Anthony; Thines, Marco; Svatoš, Aleš; Pohnert, Georg
The oomycete emphLagenisma coscinodisci hijacks host alkaloid synthesis during infection of a marine diatom Journal Article
In: Nat Commun, vol. 10, iss. 1, pp. 4938, 2019.
@article{Vallet:19,
title = {The oomycete emphLagenisma coscinodisci hijacks host alkaloid synthesis during infection of a marine diatom},
author = {Marine Vallet and Tim U H Baumeister and Filip Kaftan and Veit Grabe and Anthony Buaya and Marco Thines and Aleš Svatoš and Georg Pohnert},
doi = {10.1038/s41467-019-12908-w},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-01-01},
journal = {Nat Commun},
volume = {10},
issue = {1},
pages = {4938},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Dührkop, Kai; Fleischauer, Markus; Ludwig, Marcus; Aksenov, Alexander A; Melnik, Alexey V; Meusel, Marvin; Dorrestein, Pieter C; Rousu, Juho; Böcker, Sebastian
SIRIUS 4: A rapid tool for turning tandem mass spectra into metabolite structure information Journal Article
In: Nat Methods, vol. 16, iss. 4, pp. 299–302, 2019.
@article{Duehrkop:19,
title = {SIRIUS 4: A rapid tool for turning tandem mass spectra into metabolite structure information},
author = {Kai Dührkop and Markus Fleischauer and Marcus Ludwig and Alexander A Aksenov and Alexey V Melnik and Marvin Meusel and Pieter C Dorrestein and Juho Rousu and Sebastian Böcker},
doi = {10.1038/s41592-019-0344-8},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-01-01},
journal = {Nat Methods},
volume = {16},
issue = {4},
pages = {299–302},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2018
Thume, Kathleen; Gebser, Björn; Chen, Liang; Meyer, Nils; Kieber, David J; Pohnert, Georg
The metabolite dimethylsulfoxonium propionate extends the marine organosulfur cycle Journal Article
In: Nature, vol. 563, iss. 7731, pp. 412–415, 2018.
@article{Thume:18,
title = {The metabolite dimethylsulfoxonium propionate extends the marine organosulfur cycle},
author = {Kathleen Thume and Björn Gebser and Liang Chen and Nils Meyer and David J Kieber and Georg Pohnert},
doi = {10.1038/s41586-018-0675-0},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-01-01},
journal = {Nature},
volume = {563},
issue = {7731},
pages = {412–415},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2015
Dührkop, Kai; Shen, Huibin; Meusel, Marvin; Rousu, Juho; Böcker, Sebastian
Searching molecular structure databases with tandem mass spectra using CSI:FingerID Journal Article
In: Proc Natl Acad Sci, vol. 112, iss. 41, pp. 12580-12585, 2015.
@article{Duehrkop:15,
title = {Searching molecular structure databases with tandem mass spectra using CSI:FingerID},
author = {Kai Dührkop and Huibin Shen and Marvin Meusel and Juho Rousu and Sebastian Böcker},
doi = {10.1073/pnas.1509788112},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-01-01},
journal = {Proc Natl Acad Sci},
volume = {112},
issue = {41},
pages = {12580-12585},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2014
Rosenwasser, Shilo; Mausz, Michaela A; Schatz, Daniella; Sheyn, Uri; Malitsky, Sergey; Aharoni, Asaph; Weinstock, Eyal; Tzfadia, Oren; Ben-Dor, Shifra; Feldmesser, Ester; Pohnert, Georg; Vardi, Assaf
Rewiring host lipid metabolism by large viruses determines the fate of emphEmiliania huxleyi, a bloom-forming alga in the ocean. Journal Article
In: The Plant Cell, vol. 26, iss. 6, pp. 2689–2707, 2014.
@article{Rosenwasser:14,
title = {Rewiring host lipid metabolism by large viruses determines the fate of emphEmiliania huxleyi, a bloom-forming alga in the ocean.},
author = {Shilo Rosenwasser and Michaela A Mausz and Daniella Schatz and Uri Sheyn and Sergey Malitsky and Asaph Aharoni and Eyal Weinstock and Oren Tzfadia and Shifra Ben-Dor and Ester Feldmesser and Georg Pohnert and Assaf Vardi},
url = {https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24920329/},
doi = {10.1105/tpc.114.125641},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-06-01},
journal = {The Plant Cell},
volume = {26},
issue = {6},
pages = {2689–2707},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {ppublish},
tppubtype = {article}
}



